Soft matter
MACAL's soft matter characterization lab was established in 2020 and currently hosts 10 pieces of state-of-the-art equipment. They provide support for research carried out by research groups at and outside MMK.

Please refer the MACAL policy carefully before booking. If you have any questions, please contact Jing Li (all details under contact at end of page).
 MACAL soft matter facility policy (331 Kb)
MACAL soft matter facility policy (331 Kb)
AFM - Scanning probe microscope (MM8 AFM)
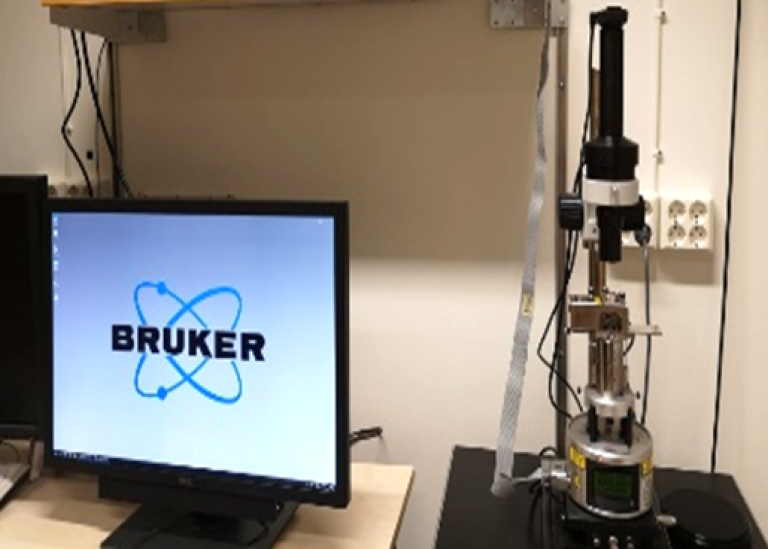

MultiMode V AFM was designed to enable measurements of small samples, such as polymers and electrochemical materials. The product now features
- Industry-leading high-speed data capture (50 MHz)
- Increased thermal tune capabilities
- High pixel density images allow observation of large structures and small features in the same image
The system performs the full range of AFM and scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) techniques to measure surface characteristics like
- Topography
- Elasticity
- Friction
- Adhesion
- Magnetic/electrical fields
The short mechanical path length between probe tip and sample enables very fast scan rates with utmost precision.
Capabilities/Accessories/Operational Modes
Capabilities/Accessories
- New NanoScope V controller
- Offers high-speed data capture (50MHz)
- Captures up to eight images simultaneously
- High-pixel-density images (5000 x 5000)
Operational Modes
- Contact Mode
- Tapping Mode
- Multimode PeakForce Quantiative Nanomechanical Mapping (MM-PFQNM)
- Lateral Force Microscopy
- Scanning Tunneling Microscopy
- Electrostatic Force Microscopy
Sample requirements
AFM samples are attached to 1.5 cm metallic disks. Samples should not exceed the size of the disk and must be less than 8 mm thick. The maximum scan scanning size is 10 microns x 10 microns and the maximum height is 2.5 microns.
User requirements
New and non experienced people wanting to get AFM training, need to study AFM theory and pass to quiz in order to be given hands on training.
- The AFM tips normally should be provided by each user.
- Users can purchase AFM cantilevers through MACAL under specific occasions, the user should contact the facility manager for a check first.
Recommended tutorials
Tutorials can be found at below link
Dynamic mechanical thermal analyzer (DMA)
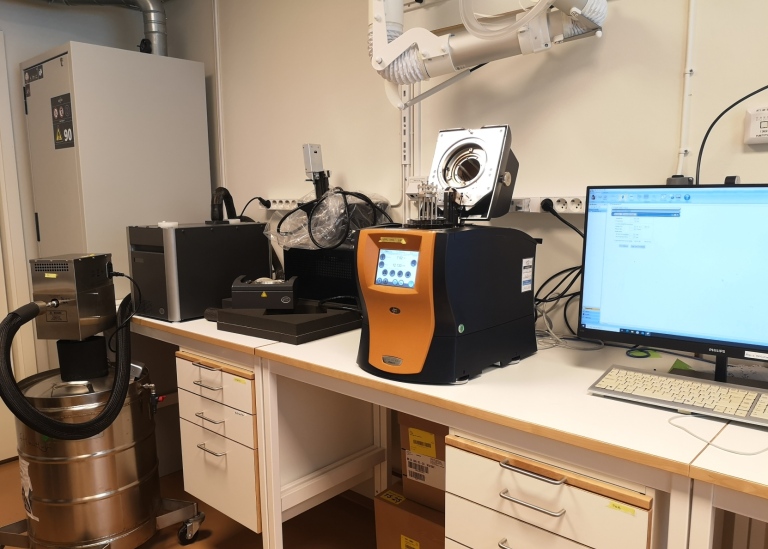

Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA) measures viscoelastic properties (storage modulus, loss modulus and tan delta peak) of polymeric materials as a function of temperature, frequency and relative humidity. The DMA has a motor and driveshaft used to apply torsional, tensile or bending stress on materials, and a linear variable differential transformer will be used to measure linear displacement.
Capabilities/Accessories
|
Deformation Modes |
|
| Maximum Force | 18 N |
| Minimum Force | 0.0001 N |
| Force Resolution | 0.00001 N |
| Frequency Range | 0.001 to 200 Hz |
| Dynamic Deformation Range | ±0.005 to 10,000 μm |
| Strain Resolution | 0.1 nm |
| Modulus Range | 103 to 3×1012 Pa |
| Modulus Precision | ± 1% |
| Tan δ Sensitivity | 0.0001 |
| Tan δ Resolution | 0.00001 |
| Temperature Range | Standard Furnace: -160°C to 600°C RH Accessory: 5°C to 120°C |
| Time-Temperature Superposition | Yes |
Typical properties and behaviors measured by the DMA 850 ((TA instrument))
- Modulus of Elasticity (E)
- Modulus of Rigidity (G)
- Complex Moduli (E*,G*)
- Storage and Loss Moduli (E’, E”, G’, G”)
- Damping Properties (tan δ)
- Glass transition
- Secondary Transitions
- Melting and crystallization
- Softening
- Relaxation behavior
- Frequency Effects
- Creep and Recovery
- Stress Relaxation
- Time-Temperature Superposition (TTS)
- Viscous flow
- Dynamic Fatigue
- Impact Strength
- Toughness
- Resiliency
- Stress-strain Curves
- Shrink Force
- Composites
- Composition of blends
- Phase Separation (Polymer Blends, Copolymers…)
- Material defects
- Effects due to fillers
- Orientation Effects
- Effects of Additives
- Aging (physical or chemical)
- Gelation
- Crosslinking Reactions
- Crosslink Density
- Mullins Effect
Testing mode
- Stress-Strain Curves
- Creep and Stress Relaxation
- Isostress and Isostrain
Examples/Application areas
1. Jonoobi, M., Harun, J., Mathew, A. P. & Oksman, K. Mechanical properties of cellulose nanofiber (CNF) reinforced polylactic acid (PLA) prepared by twin screw extrusion. Compos. Sci. Technol. 70, 1742–1747 (2010).
2. Moreno, A.; Morsali, M.; Sipponen, M. H. Catalyst-Free Synthesis of Lignin Vitrimers with Tunable Mechanical Properties: Circular Polymers and Recoverable Adhesives. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, acsami.1c17412. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.1c17412.
Useful links
Tensile testing system (Instron)
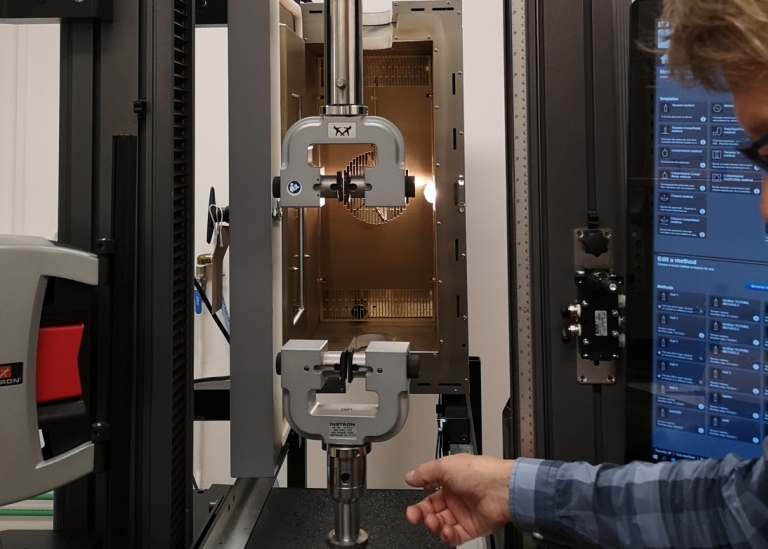

Universal testing machine for the determination of the mechanical properties of ceramic, metal and polymer based samples in tensile, compression, bending modes.
Capabilities/Accessories
- Model: Instron 5960 dual column table top
- Load cells: 10 kN, 1 kN, 100 N
Fixtures
- Tensile grips: Pneumatic grips for soft materials and elastomers, Wedge grips for rigid materials, Thin film grips
- Compression platen
- 3-point bending fixture
- Additional accessories
- Video extensiometer (with DIC integration)
- Temperature chamber (-100 to 350°C)
- Temperature controlled bath with pneumatic tensile grips and compression platens
Useful links
Contact angle meter, Drop Shape Analyzer – DSA25E (KRÜSS instruments)
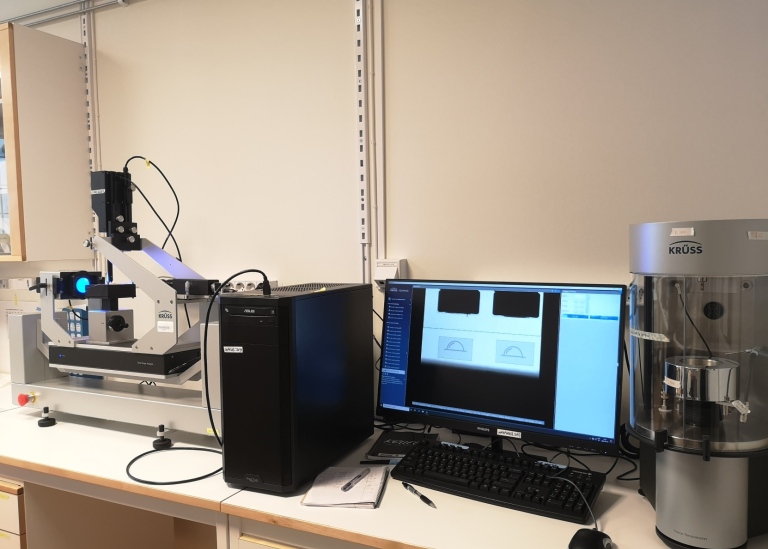
The Drop Shape Analyzer – DSA25 is designed for determining the wettability of solids by means of the contact angle as well as the surface tension of liquids such as coating substances or adhesives. Thanks to the combination of speed and versatile evaluation options, the analyses give quick feedback to pretreatment steps in quality control but also allow assessing the resulting adhesion. Contact angle instrument is equipped with a digital camera to record the droplet morphology and measure the angle and evaluate the wettability and adhesion.
Capabilities/Accessories
- Quick and versatile dosing for surface free energy and surface tension
- Reliable drop shape analysis thanks to high imaging quality
- Maximum repeatability and comprehensive adhesion analysis
Measuring methods
Drop shape analysis (DSA): The contact angle is measured using the image of a sessile drop at the points of intersection (three-phase contact points) between the drop contour and the projection of the surface (baseline).
Examples/Application areas
Karim, Z., Hakalahti, M., Tammelin, T. & Mathew, A. P. In situ TEMPO surface functionalization of nanocellulose membranes for enhanced adsorption of metal ions from aqueous medium. RSC Adv. 7, 5232–5241 (2017).
Useful links
Surface tensiometer for surface tension measurement
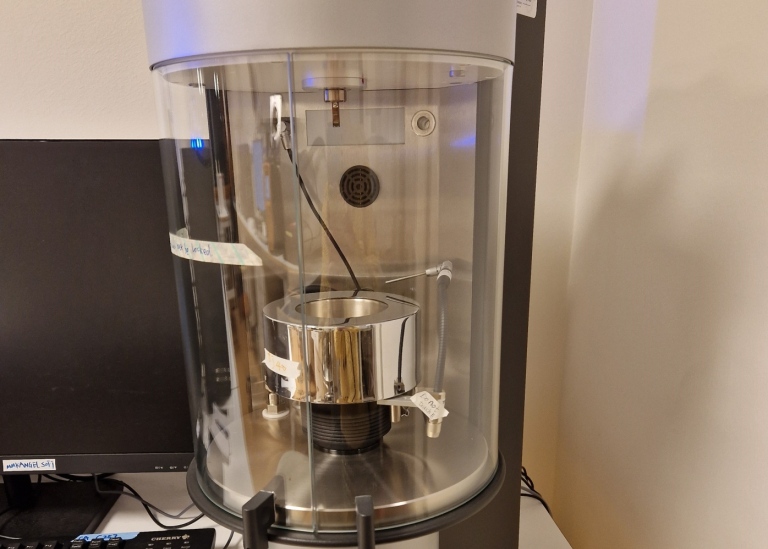

The Force Tensiometer – K100 performs high precision, automatic and reliable measurements of surface tension and interfacial tension, critical micelle concentration CMC and contact angle on solids, fibers and powders. With high-quality components and a uniquely wide range of methods, the instrument carries out many tasks in the field of surfactant analysis and wetting measurement for your quality assurance or research. The simple changeover between different measuring methods takes place entirely without reconfiguring the instrument. The surface tension measurement is an automatic system to measure surface energy and will be based on tensiometer method using ring and plates.
Capabilities/Accessories
- Determination of the effectiveness and efficiency of surfactants by CMC measurement
- Wetting behavior of tablets, pharmaceutical active ingredients and excipients
- Wetting and adhesion of coatings
- Development of cosmetic products
- Wetting of fiber bundles and textiles
- Checking of surface modifications
Measurement method
- Wilhelmy plate method: The force acting in the tensile direction when moving a plate-shaped solid vertically in a liquid is measured. This force depends on the contact angle as well as on the surface tension and the wetted length. Instrument: K100
- Powder contact angle measurement using the Washburn method: The increase in weight of an immersed powder-filled tube is measured with respect to time. The rate of rise of the liquid column depends, among other things, on the contact angle. Instrument: K100
Background knowledge and useful links
Critical surface tension
According to the Zisman method, the critical surface tension is the surface tension at which a liquid just completely wets a solid. The surface tension of different liquids is plotted against the cosine of the contact angle θ in order to determine the critical surface tension. The value of the surface tension from the regression equation for cos θ = 1 (contact angle = 0°) corresponds to the critical surface tension.
Dynamic surface tension
The dynamic surface tension (SFT) or interfacial tension (IFT) is the value of the SFT or IFT referred to a particular surface age or interface age. In the case of liquids with surface-active substances (surfactants), this can differ from the equilibrium value.
Viscometer
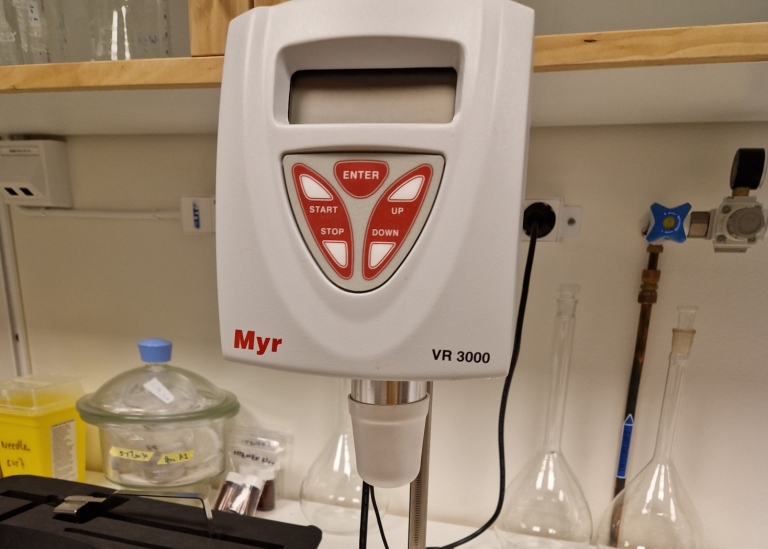

The VR 3000 MYR Viscometers, models V2 R, are rotational viscometers for the fast determination of viscosity as specified in ISO 2555 and other ASTM norms. The Instrument offers viscosity measurements which are 100% compatible with the Brookfield method and permits to carry out comparative measurements in accordance to recognized standards in quality control laboratories. All models are available in three different versions: Version "L" for low to medium viscosity, version "R" for medium to high viscosity and version "H" for high to very high viscosity.
Model V2 has 2 more speeds –and consequently a wider viscosity range-, bidirectional interface RS232 and optionally, software ViscosoftPlus for the automated control of viscometer and the issuing of rheological studies.
Capabilities/Accessories
Displayed Data
| Displayed Data |
|
| Speed Selected | rpm |
| Spindle Used | spindle reference |
| Dynamic Viscosity | mPas or cP (in version H, dPas or P) |
| Full Scale Percentage |
% |
| Sample Temperature | ºC or ºF |
| Auto Range To Display Viscosity Limits | mPas o cP (in version H, dPas or P) |
| Shear Rate (SR) (With Special Spindles) | 1/sec (only in V2 version) |
| Shear Stress (SS) (With Special Spindles) | N/m2 or dyne/cm2 (only in V2 version |
Densimeter
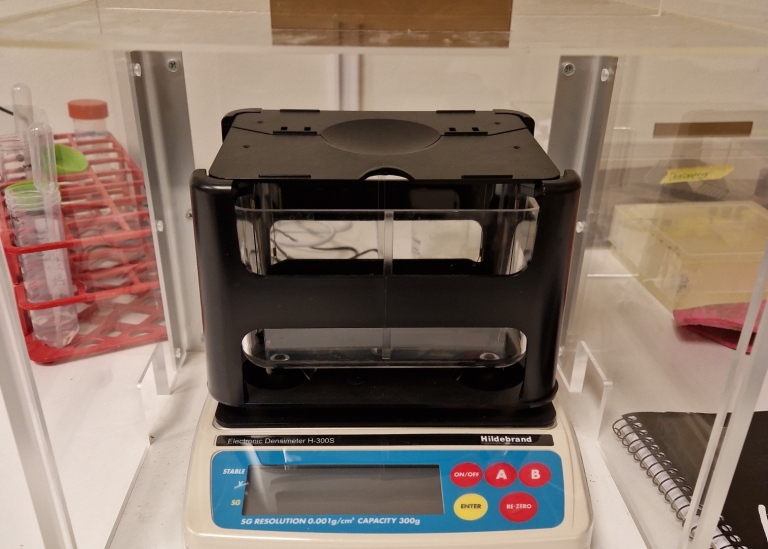

The Hildebrand Densimeter Model H-300 S is a cost efficient instrument for calculating the specific gravity with a superior resolution of 0.001. The system is suitable for checking plastics, rubber, films, liquids, sintered metals, ceramics, glass and other non-metal materials. The value is displayed automatically after the elapsed time.
Capabilities/Accessories
- Density/resolution 0,001 g/cm3
- Range: 0,01...300 g
- Easy to operate
- Automatoc calculation of density
- Compensation of water temperature
- Able to measure floating sample in water
- The volume of solid sample be measured
- Dimensions: 190 mm x 218 mm x 170 mm
- Net Weight: 1,54 kg
Useful link
Refractometer
Abbe Refractometer NAR-1T SOLID is suitable to measure the Refractive Index Scale and the BRIX scale for liquid and solid samples.
Capabilities/Accessories
| Specifications | |
| Model | NAR-1T SOLID |
| Cat.No. | 1212 |
| Range | Refractive index (nD) : 1.3000 to 1.7000 Brix : 0.0 to 95.0% |
| Minimum Scale | Refractive Index (nD) : 0.001 Brix : 0.5% |
| Accuracy | Refractive index (nD) : ±0.0002 Brix : ±0.1% |
| Average dispersion value | nF-nC (to be calculated according to conversion table) |
| Measurement Temp. | 5 to 50゚C |
| Light source | LED (Approximating to wavelength of D-Line) |
| Dimensions & Weight | 13×18×23 cm, 2.5 kg (Refractometer) 10×11×7 cm, 0.5 kg (Thermometer) |
Useful links
Rheometer (MCR Rheometer 301)
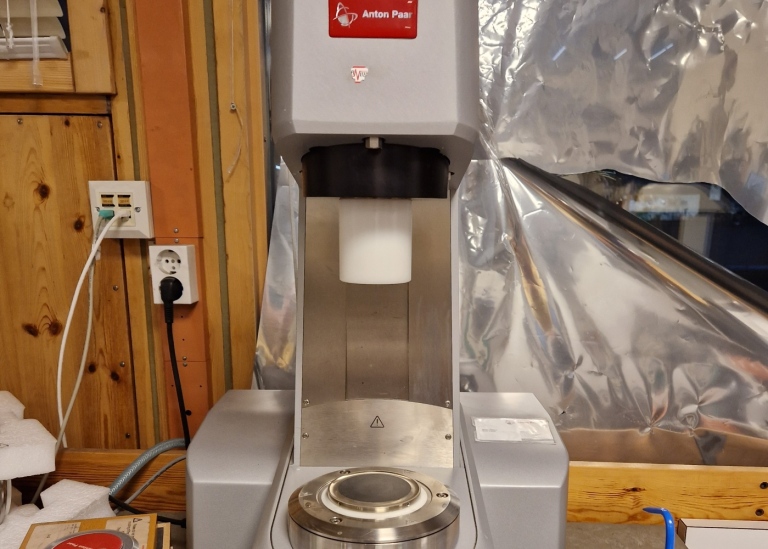

Rheology is the science of deformation and flow of materials. Often the materials are exposed to different external forces. In practice we have the forces like is for example gravitational which have an influence on process as sagging or sedimentation and shear forces that are acting for example when we want to bring material with polishing tool on wall. However, every successful application requires its own behaviour of material.
Optimization of all the major components of modern Reometer Physica 301 MCR: motor, air bearing, the electronic
control, compact frame based on the concept art technology, economics, modern design integrates both, so mechanical, and electronic control components in a single instrument.
Capabilities/Accessories
Specifications
- MCR Rheometer 301 is compact system with air bearings and high-performance synchronous motor with direct EC control rotor motion and 100% control of the rotor field with continuous torque available, without thermal heating, which allows rheological measurements at high quality levels.
- Possible performance tests with oscillating or regulation. adjustment of shearing even in samples with low viscosity. It allows measurement at low torques 0.01 μNm and divergence sensor or 0.1 μrad. perceived burden of 10nNm (example: such as the stroke hair n fingertip arm) and therefore allows measurement of the extremely fragile structures at extremely small shear speeds and voltages.
- Fast and automatic identification of measuring geometries (measurement systems) and systems termostatiranja and tempering, and immediate wireless transmission of technical parameters of the electronic Rheometers.
Rheometers capacity
Requirements:
Min. Torque (torque) 0.01 μNm, Max. Torque (torque) 200 μNm, resolution 0.001 μNm torque, set an angle of divergence of 0.1 μrad sensor, sensor resolution angle deviation 0.012 μrad
Min speed (measurement method: adjustable shear stress) 10E-7 1/min, Min speed (mode measurement: adjustable shear rate) 10E-6 1/min, 3000 1/min Max.speed, Min. frequency: 10E-5 Hz, Max. Frequency: 100 Hz, the range of normal forces of 0.01 to 50 N, resolution normal force of at least 0.002 N
Rheology is the science of deformation and flow of materials. Often the materials are exposed to different external forces. In practice we have the forces like is for example gravitational which have an influence on process as sagging or sedimentation and shear forces that are acting for example when we want to bring material with polishing tool on wall. However, every successful application requires its own behaviour of material.
Optimization of all the major components of modern Reometer Physica 301 MCR: motor, air bearing, the electronic
control, compact frame based on the concept art technology, economics, modern design integrates both, so mechanical, and electronic control components in a single instrument.
Specifications oscillating MCR Rheometers 301:
- MCR Rheometer 301 is compact system with air bearings and high-performance synchronous motor with direct EC control rotor motion and 100% control of the rotor field with continuous torque available, without thermal heating, which allows rheological measurements at high quality levels.
- ·Possible performance tests with oscillating or regulation. adjustment of shearing even in samples with low viscosity. It allows measurement at low torques 0.01 μNm and divergence sensor or 0.1 μrad. perceived burden of 10nNm (example: such as the stroke hair n fingertip arm) and therefore allows measurement of the extremely fragile structures at extremely small shear speeds and voltages.
- Fast and automatic identification of measuring geometries (measurement systems) and systems termostatiranja and tempering, and immediate wireless transmission of technical parameters of the electronic Rheometers.
Courses/training
AFM PhD Course
Course responsible: Jing Li
Course name: KZ41005, Instroduction into Atomic Force Mictroscopy. 2.0 ECTS
The course is given once a year in spring term.
The course introduces theories of AFM and scanning probe microscopic methods and their applications in nanotechnology and nanoscience. The exercise and hands-on practical sessions include both data acquisition and analysis.
Instrument training
Please contact lab manager
Recharge rates
MMK User |
||
No assistance (SEK) |
Operator assistance (SEK) |
|
AFM |
1200/4 hrs | +300/hr |
Instron |
225/hr | +250/hr |
DMA |
300/hr | +300/hr |
Contact angle |
150/hr | +250/hr |
Surface tension |
225/hr | +250/hr |
Rheometer |
300/hr | +300/hr |
Viscometer |
75/hr | +250/hr |
Densimeter |
75/hr | +250/hr |
Refractometer |
75/hr | +250/hr |
External User, academic |
||
No assitance (SEK) |
Operator assistance (SEK) |
|
AFM |
750/hr | +800/hr |
Instron |
450/hr | +500/hr |
DMA |
750/hr | +1000/hr |
Contact angle |
450/hr | +500/hr |
Surface tension |
450/hr | +1000/hr |
Rheometer |
750/hr | +500/hr |
Viscometer |
150/hr | +500/hr |
Densimeter |
150/hr | +500/hr |
Refractometer |
150/hr | +500/hr |
Industrial User |
||
No assitance (SEK) |
Operator assistance (SEK) |
|
AFM |
1500/hr | +1200/hr |
Instron |
1050/hr | +1000/hr |
DMA |
1500/hr | +1500/hr |
Contact angle |
1050/hr | +1000/hr |
Surface tension |
1050/hr | +1000/hr |
Rheometer |
1500/hr | +1500/hr |
Viscometer |
450/hr | +1000/hr |
Densimeter |
450/hr | +1000/hr |
Refractometer |
450/hr | +1000/hr |
Contact

- Visiting address
- C 520
- Svante Arrhenius väg 16 C
Jing Li, Research Engineer
Last updated: June 18, 2024
Source: MMK

